
Introduction
Immersive Virtual Reality (IVR) has become a powerful tool in education, offering a natural and engaging learning experience. This thesis presents a case study conducted at the College of Technology in Rotterdam, focusing on a Secondary Vocational Education Level 2 course teaching computer assembly. For this course, Virtual TechLab was developed, an IVR application by Changefied, aiming to enhance computer assembly skills. Recognizing the importance of collaboration in learning, especially in IVR environments, this research investigates the impact of multiplayer capabilities in Educational Virtual Reality Games (EVRGs) on learning efficiency and student motivation.
Demonstration video of the VR application
Data collection
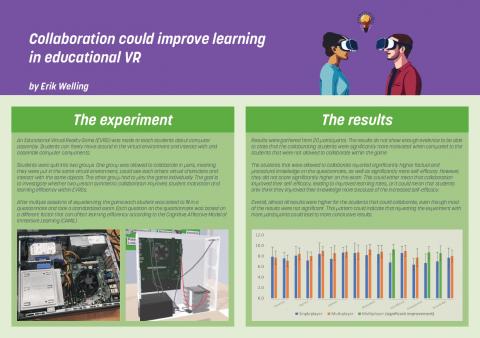
Data collection involves two groups, one group that plays the game individually and a group that is allowed to play the game with two-player symmetrical collaboration. The research evaluates learning outcomes through a standardized exam and subjective metrics using a questionnaire based on the Cognitive Affective Model of Immersive Learning (CAMIL). The hypotheses test the significance of collaboration in improving motivation and learning efficiency.
Findings
Motivation levels, as measured by the questionnaire, did not show a significant increase between the individual group and their collaborating peers.
Comparing exam scores between the two groups did not yield a significant difference. However, students that were able to collaborate reported significantly enhanced factual and procedural knowledge on the questionnaire as well as significantly improved levels of self-efficacy.
Patterns in the results suggest that further research with larger sample size could allow for more conclusive results.
Contributions
The thesis gives insight into how collaboration affects the different aspects that influence learning efficiency. Even though they are not fully conclusive, the results point toward an improvement in learning efficiency when collaborating. This thesis will hopefully spark the interest of other researchers to dive deeper into this subject matter and might eventually lead to more widespread adoption of such features in educational games, potentially improving the quality of gamified education in general. While the case study focuses on computer assembly, the results could potentially benefit other educational domains as well.
Ethical considerations disclaimer
Prior to commencing the research, an ethics quick scan was conducted by the University of Utrecht to assess the ethical implications of the study.
The quick scan highlighted two crucial ethical considerations that require careful attention. The first concerns a possible conflict of interest due to my partial ownership in the company for which the research is conducted. Consequently, there exists a potential for bias towards favorable outcomes in the course of my experiments. To address this concern, I implemented measures to mitigate any bias.
To ensure impartiality, I maintained regular communication with my impartial supervisor throughout the research. Additionally, I employed objective measurements wherever feasible, particularly in areas where a favorable outcome may be desired. Where subjective conclusions are necessary, I transparently disclose the underlying data and approach the conclusions with honesty, always mindful of this potential bias. By diligently combining these efforts, I am confident in my ability to approach the research in a sincere and unbiased manner.
The second ethical consideration pertains to involving minors under the age of eighteen in the study. Adhering to ethical standards, all participating students are presented with an information sheet and a consent form to ensure voluntary participation. Additionally, parents or legal guardians of minors must also provide explicit consent through the means of the consent form. These consent forms and information sheets were provided in both Dutch and English.
